蘿蔔與坑 —— JavaScript 的 Hash Table 是什麼?
此篇為 Udemy - Master the Coding Interview: Data Structures + Algorithms 課程筆記。
上篇介紹了如何用 JavaScript 的 Object,實作 Array 的資料結構,這篇則要來解釋 JavaScript 最核心的概念——物件(Object)。
講到 JavaScript 當中的物件,你可能會想到的是像以下的資料結構:
let user = {
id: 1,
name: "John Doe",
age: 20,
};
由此可以看出 Object 是由key: value組成,那在 RAM 當中,他又是怎麼被儲存的?這時我們必須要了解 Hash Tables 的資料結構。
Hash Tables
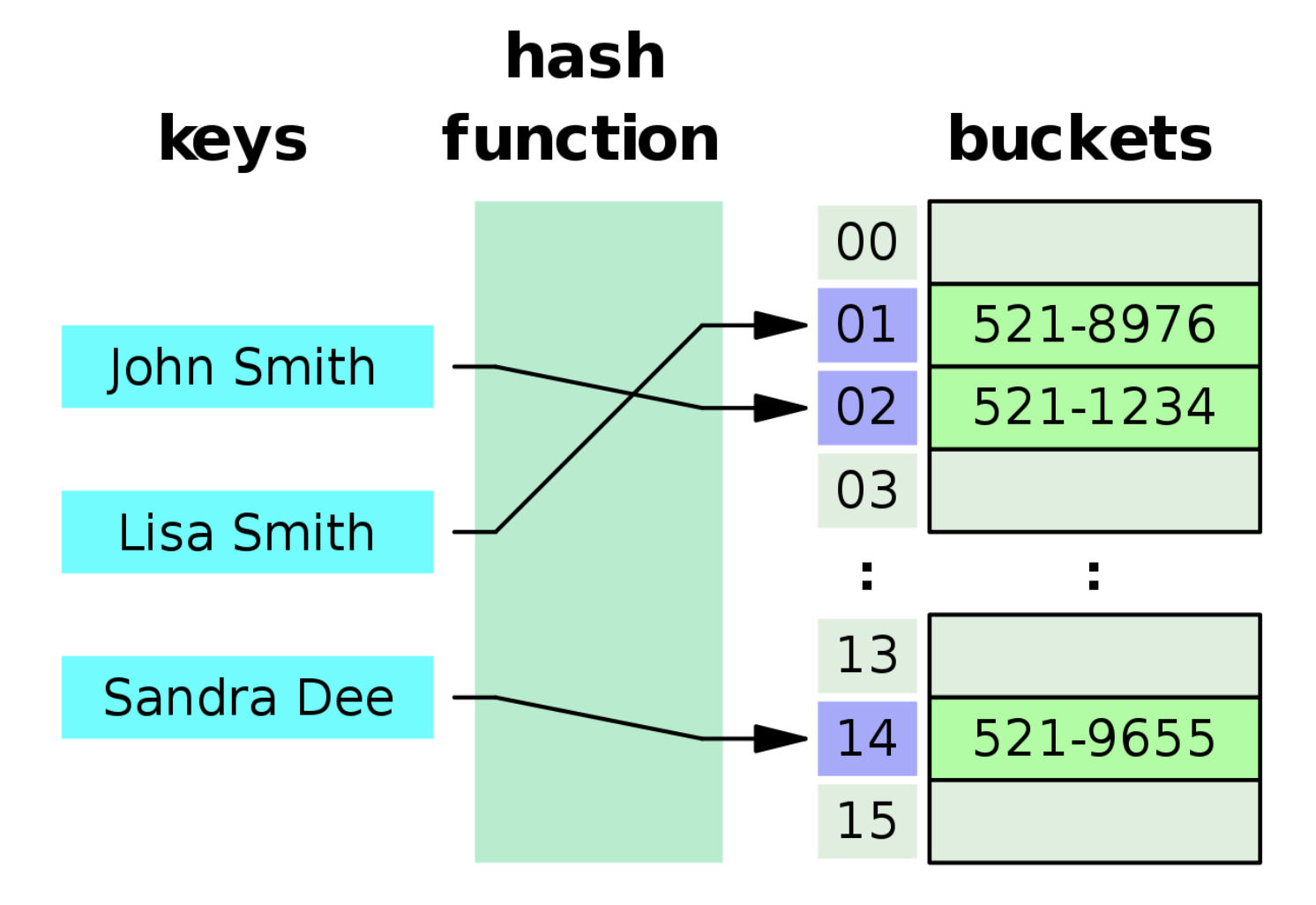
Hash Tables 在不同語言當中,有不同的實現方式,而在 JavaScript 當中,Hash Tables 這個資料結構就是以 Object 的方式呈現。
Hash Tables 的運作方式,可以把他想成,假設我有一塊空地。這塊空地上有 100 個坑。而我手上剛好有 10 個蘿蔔,現在我要把這 10 個蘿蔔放進去這些坑裡面。
那問題來了,我要怎麼決定哪個蘿蔔放進哪個坑裡面?
這時我決定用一個轉盤,當轉盤轉到 2,我就把第一個蘿蔔放在 2 號坑,當轉盤轉到 78,我就把第二個蘿蔔放到 78 號坑。
沒錯,看到這裡,你已經學會 Hash Tables 的運作方式了。
我們可以把那塊「空地」想成記憶體,「坑」想成記憶體位址,「蘿蔔」想成資料,而轉盤想成 hash function。當我想把一對key: value塞進去記憶體時,會將 key 放進 hash function,進而得出我想要把這個資料放在哪一個記憶體位址。
但是,當我第一個轉盤轉到 2 的時候,我把蘿蔔放到 2 號坑,那我下一次轉盤也轉到 2 的時候,我的蘿蔔還是放在 2 號坑嗎?
這就是 hash collision,在 JavaScript 裡,當遇到這種情況的時候,答案是「是」,他可以放在同一個坑裡。並且會用 Linked List 的方式存在這個記憶體位址。
不過,這些 hash function 和 hash collision 遇到的問題,其實語言本身都已經幫我們處理好了,所以我們平常在 coding 的時候,不會遇到這些問題。
Implementation
接下來我們也要來挑戰,用 JavaScript 來實作一個 Hash Tables 的 Class。
首先在 constructor 裡面,建立一個 data 變數,並可以傳入 size 來決定這個 hash table 的大小。
class HashTables {
constructor(size) {
this.data = new Array(size);
}
}
接著我們要在 Class 中新增 hash function,這個 function 會接收 key 值,並決定要將這個資料放在 hash table 的哪一個位址。
_hash(key) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash % this.table.length;
}
在這裡讓傳進來的 key 當中的每一個字母跑迴圈,透過charCodeAt()轉成數字後並相加,就可以得出那個 key 的 hash。
假如我想要存一個apple: 500的資料,apple這個 key 就會經過 function 後得出一個 hash。最後需要hash除以this.table.length的餘數,是為了確保這個 hash 值是落在我擁有的記憶體位址範圍裡面。
比如 hash = 102 時,我的 hash table 只有 100 個位址,因此我用 102 % 100 = 2 的方式,決定將這個資料放在 2 號坑。而_hash會加底線是為了表明這是一個 private function。
接下來繼續加上一些基本的 Object 能使用的 method:
Set
首先,要 set 一個資料到 hash table 裡面,必須將傳進來的 key 經過 hash function 得到到放進去的位址。接著在這個位址塞進一個空陣列(此處以 Array 為示範,而非 Linked List)。
這個空陣列就是剛剛所說的「坑」,push 就是將蘿蔔塞進去坑的動作,最後回傳這個 hash table。
set(key, value) {
let address = this._hash(key);
if (!this.data[address]) {
this.data[address] = [];
}
this.data[address].push([key, value]);
return this.data;
}
Big O: O(1)
藉由 Hash 就能快速新增 key: value
Get
接著要實作get(),首先可以從 key 找到對應的 hash 位址,得到對應的「坑」(陣列)的資料。
但因為這個「坑」(陣列)可能不只一個資料,所以要用迴圈去比對一樣的 key,就可以找到 key 對應的 value。若找不到則回傳 undefined。
get(key) {
const address = this._hash(key);
const currentBucket = this.data[address];
if (currentBucket) {
for (let i = 0; i < currentBucket.length; i++) {
if (currentBucket[i][0] === key) {
return currentBucket[i][1]
}
}
}
return undefined;
}
Big O: O(1)
大部分的情況下,沒有 hash collision,一個 address 只有一個 key: value,Big O 為 O(1),藉由 Hash 就能快速定位要找資料。
若有 hash collision,就必須跑迴圈,Big O: O(n)
Keys
Object.keys()可以用來取得 Object 所有的 key。
這裡我們假設每一個坑都只有一個蘿蔔的情況,將 this.data 跑迴圈,去檢查是否所有的 hash 位址都有東西。
如果有東西,我要去取得這個「坑」(陣列)裡面的 key。
keys(){
const keysArray = [];
console.log(this.data.length);
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++){
if(this.data[i]){
// 第 i 號的坑的第一個 pair
keysArray.push(this.data[i][0][0])
}
}
return keysArray;
}
Big O: O(n)
需將 this.data 跑迴圈,去檢查是否所有的 hash 位址都有東西。
全部的 Class 看起來像這樣:
class HashTable {
constructor(size) {
this.data = new Array(size);
}
_hash(key) {
let hash = 0;
for (let i = 0; i < key.length; i++) {
hash = (hash + key.charCodeAt(i) * i) % this.data.length;
}
return hash;
}
set(key, value) {
let address = this._hash(key);
if (!this.data[address]) {
this.data[address] = [];
}
this.data[address].push([key, value]);
return this.data;
}
get(key) {
const address = this._hash(key);
const currentBucket = this.data[address];
if (currentBucket) {
for (let i = 0; i < currentBucket.length; i++) {
if (currentBucket[i][0] === key) {
return currentBucket[i][1];
}
}
}
return undefined;
}
keys() {
const keysArray = [];
console.log(this.data.length);
for (let i = 0; i < this.data.length; i++) {
if (this.data[i]) {
keysArray.push(this.data[i][0][0]);
}
}
return keysArray;
}
}
const myHashTable = new HashTable(50);
myHashTable.set("grapes", 10000);
myHashTable.set("grapes", 10000);
myHashTable.get("grapes");
myHashTable.set("apples", 9);
myHashTable.get("apples");
myHashTable.keys();
最後,在 JavaScript 除了一般的let obj = {}以外,還有另外兩個特別的 Object,分別是Map和Set。
Object、Map、Set
Object
JavaScript 的 Object 在新增時是沒有順序性的,不像 Array 那樣從 0 開始,往上增加。
另外,Object 裡的 prototype,如hasOwnProperty()是可以被改寫的。
const obj = {};
obj.name = "Nathan";
obj.hasOwnProperty = true;
console.log(obj.hasOwnProperty("name"));
// Error: obj.hasOwnProperty is not a function
Map
而 Map 的運作方式則是跟一般 Object 不太一樣,Map 在 insert 資料時是有順序性的,並且不能覆寫他的 prototype。
const collection = new Map();
collection.set("Nathan", "555-0182");
collection["size"] = false;
console.log(collection.get("size")); // undefined
console.log(collection.size); // 1
Set
Set 跟 Map 的運作方式很像,insert 資料時是有順序性的,只是 Set 只會儲存 key,沒有 value。
Set 裡面的 key 絕對不會重複,因此如果要確認 Array 裡面的值有沒有重複,可以用Set().size來檢查。
let a = [1, 2, 3, 3, 5];
function hasDuplicate(arr) {
return new Set(arr).size !== arr.length;
}
hasDuplicate(a); // true
以上就是 Hash Tables 的介紹,以及用 JavaScript 來實作 Hash Table Class 的方式!
Pros & Cons
- Pros
- Fast lookup (good collision resolution needed)
- Fast inserts
- Flexible keys (not only number (Array))
- Cons
- Unordered
- Slow key iteration (Object.keys())
Reference
Udemy - Master the Coding Interview: Data Structures + Algorithms
